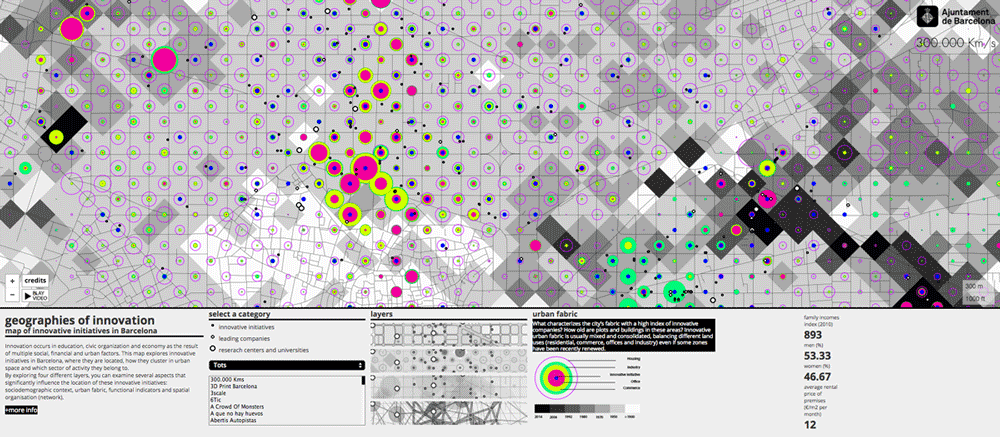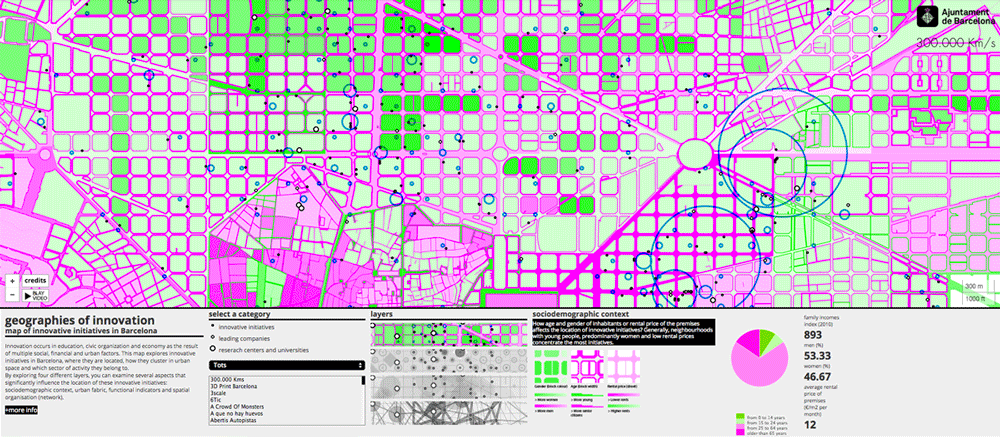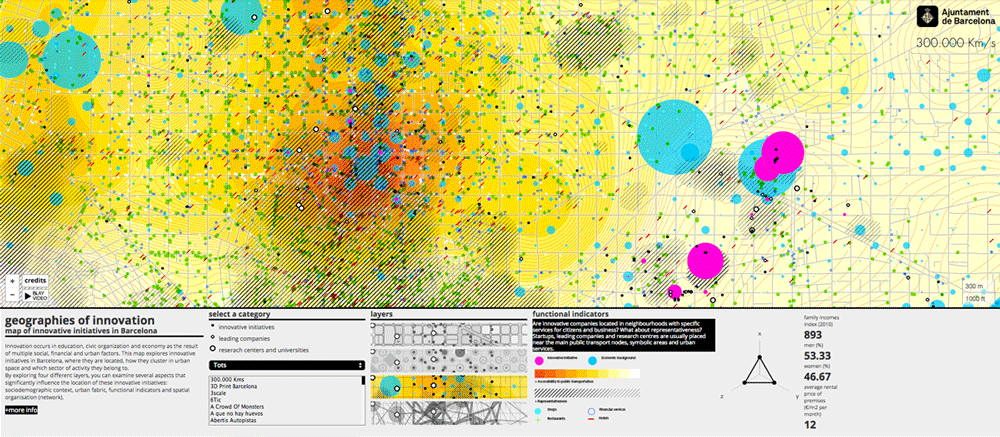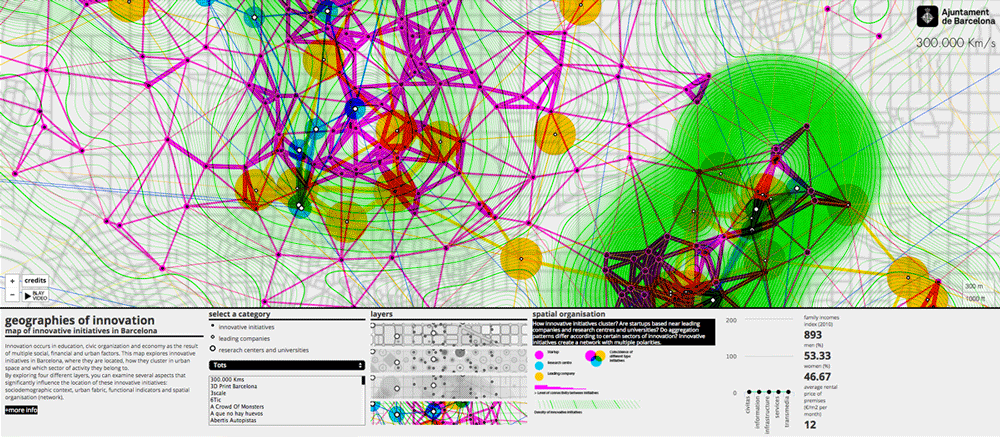
Map of innovative initiatives in Barcelona.Innovation occurs in education, civic organization and economy as the result of multiple social, financial and urban factors. This map explores innovative initiatives in Barcelona, where they are located, how they cluster in urban space and which sector of activity they belong to.
By exploring four different layers, you can examine several aspects that significantly influence the location of these innovative initiatives: socio-demographic context, urban fabric, functional indicators and spatial organization (network).
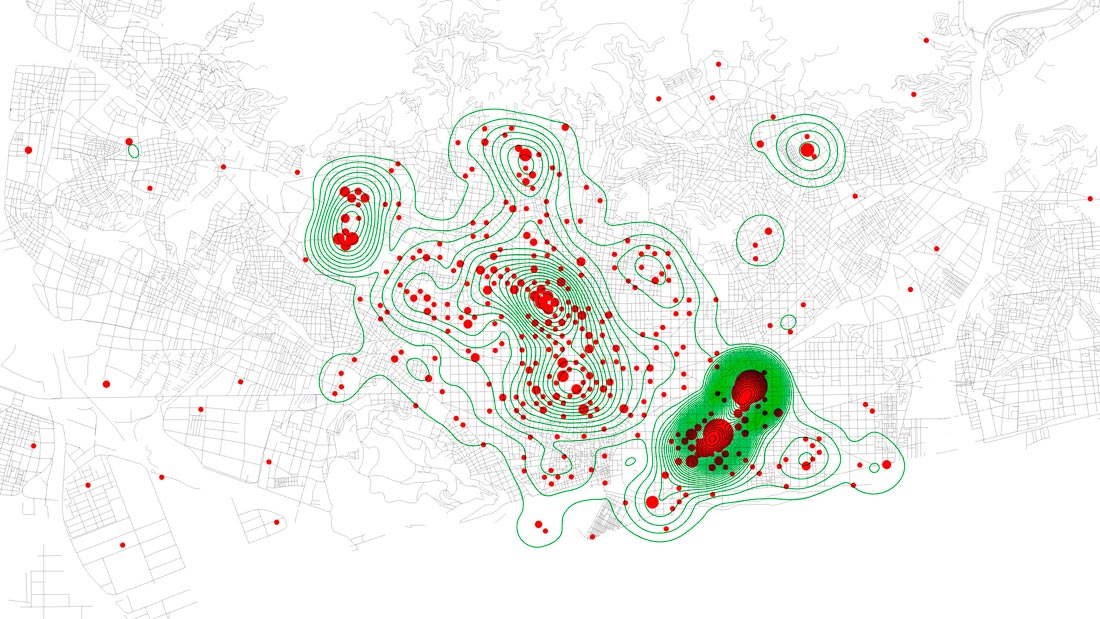
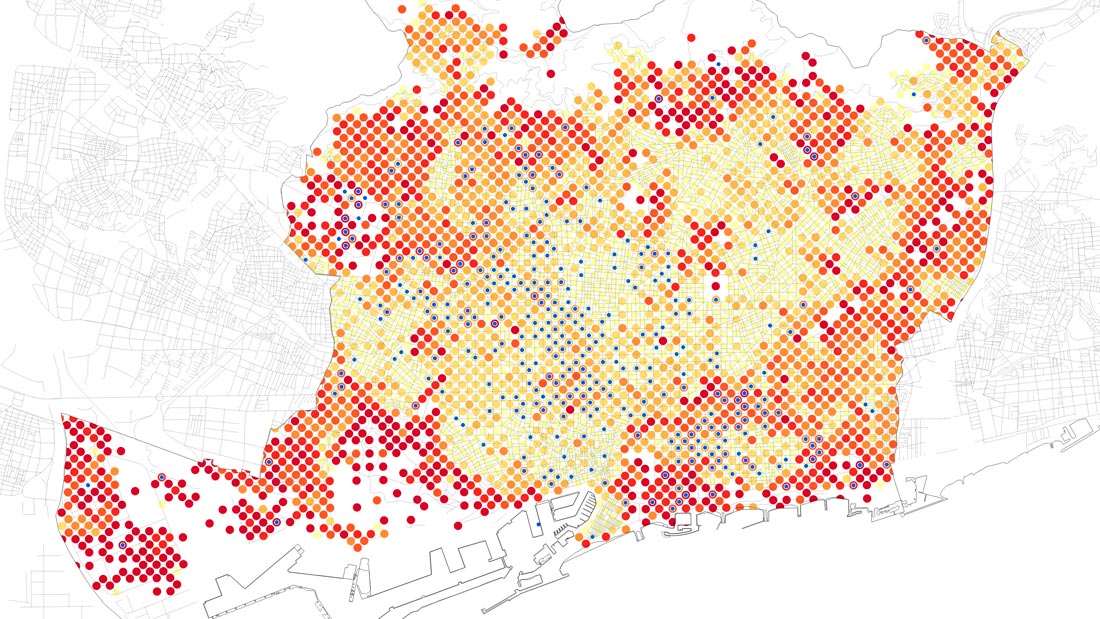
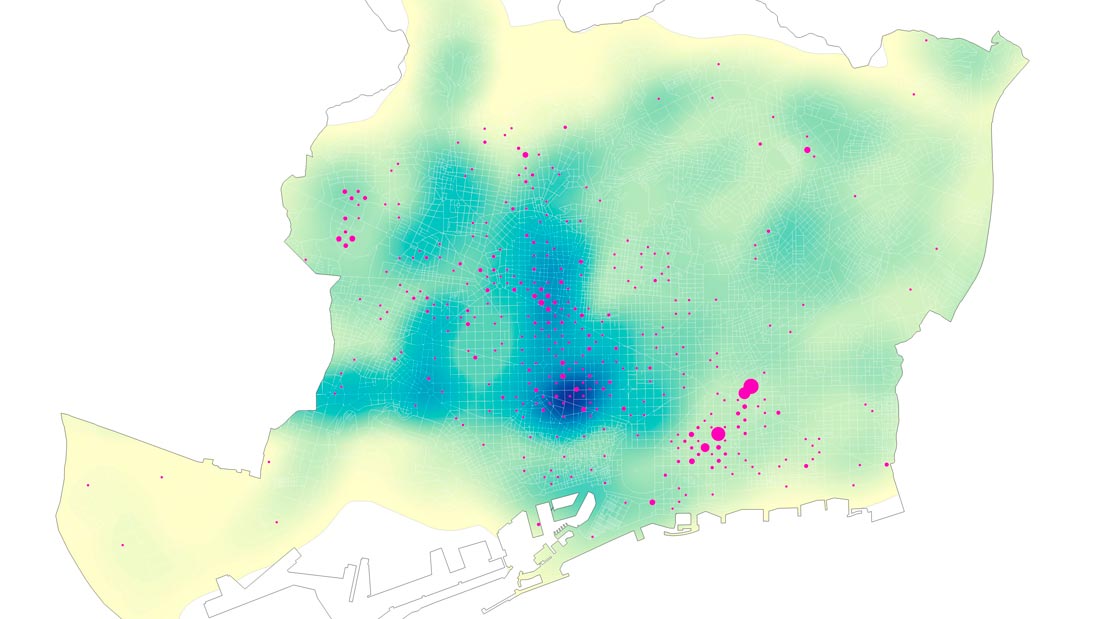
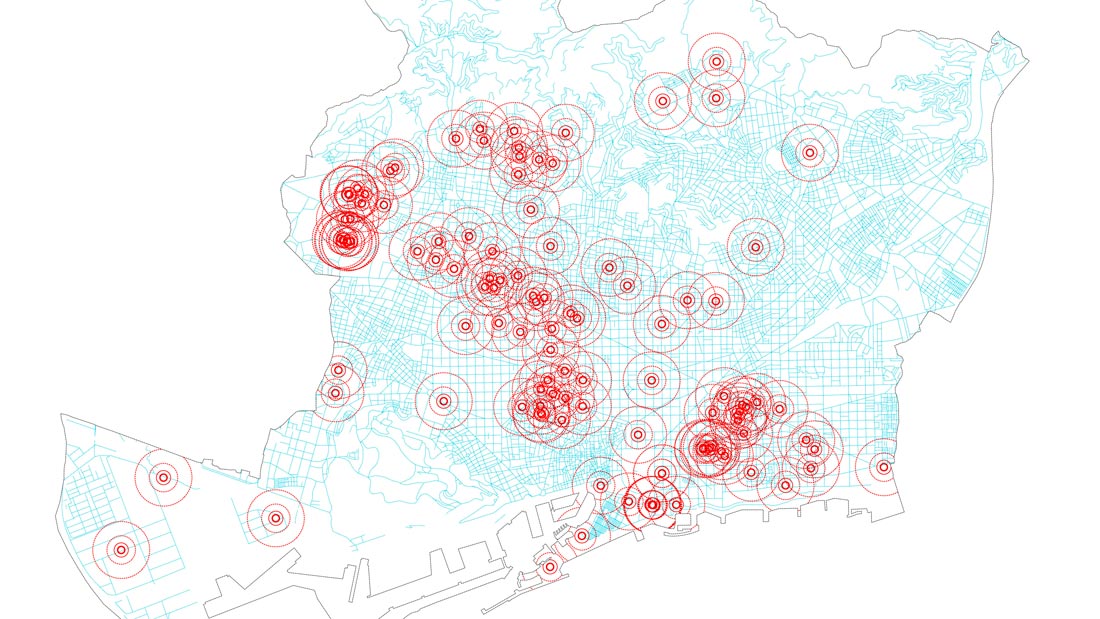
Topography according to the density of innovative initiatives.
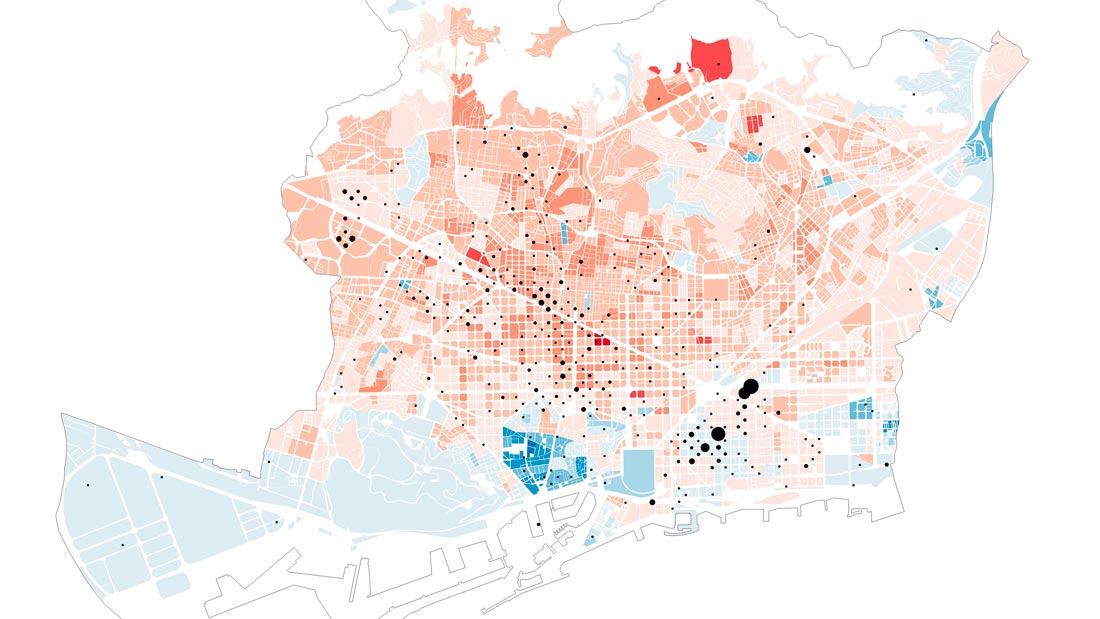
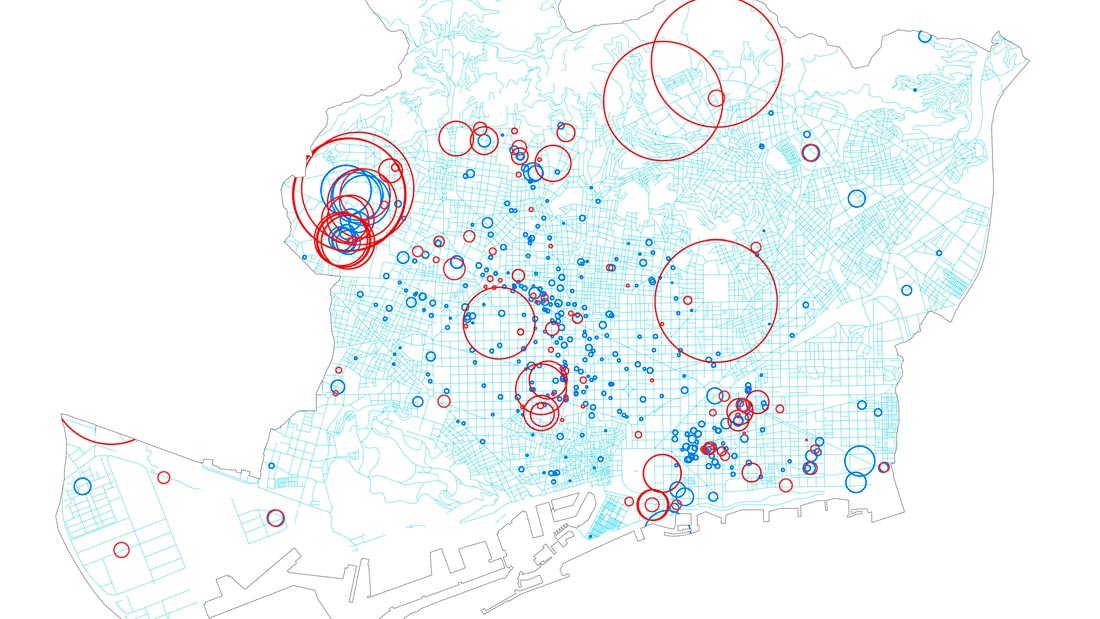
Sociodemographic context, gender. Proportion of women (red) and men (blue).
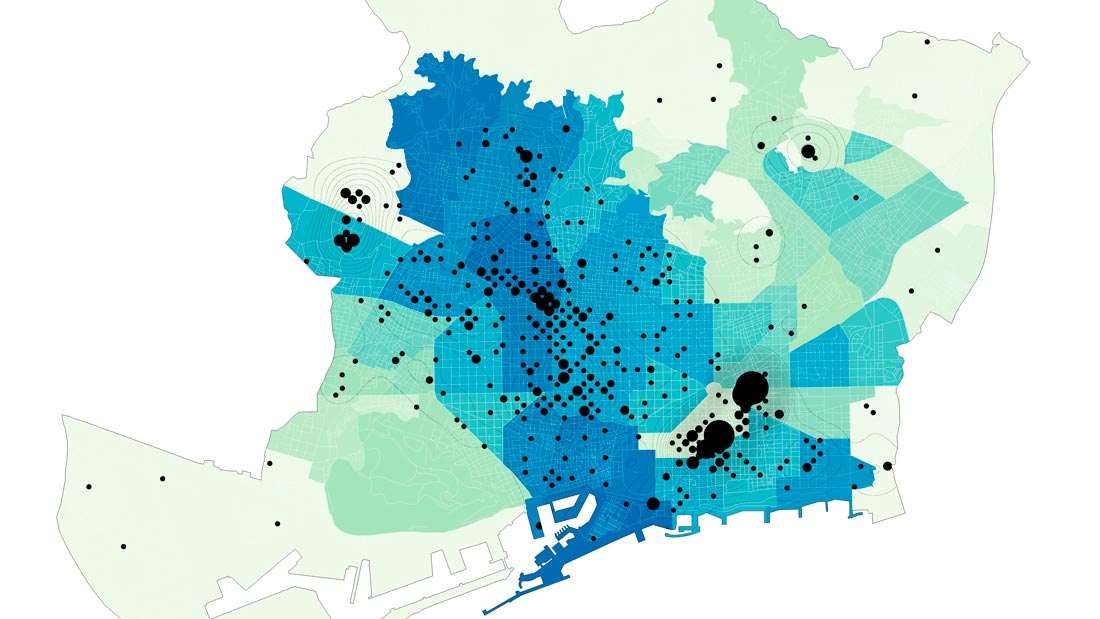
Economic background. Rental price of premises.
In recent years, Barcelona has focused on research and innovation as pillars of urban economic development. The study “Geographies of innovation” aims to assess the urban conditions for a suitable implementation of innovative initiatives. Beyond their individual success, the impact of research and innovation facilities is evaluated on an urban scale.
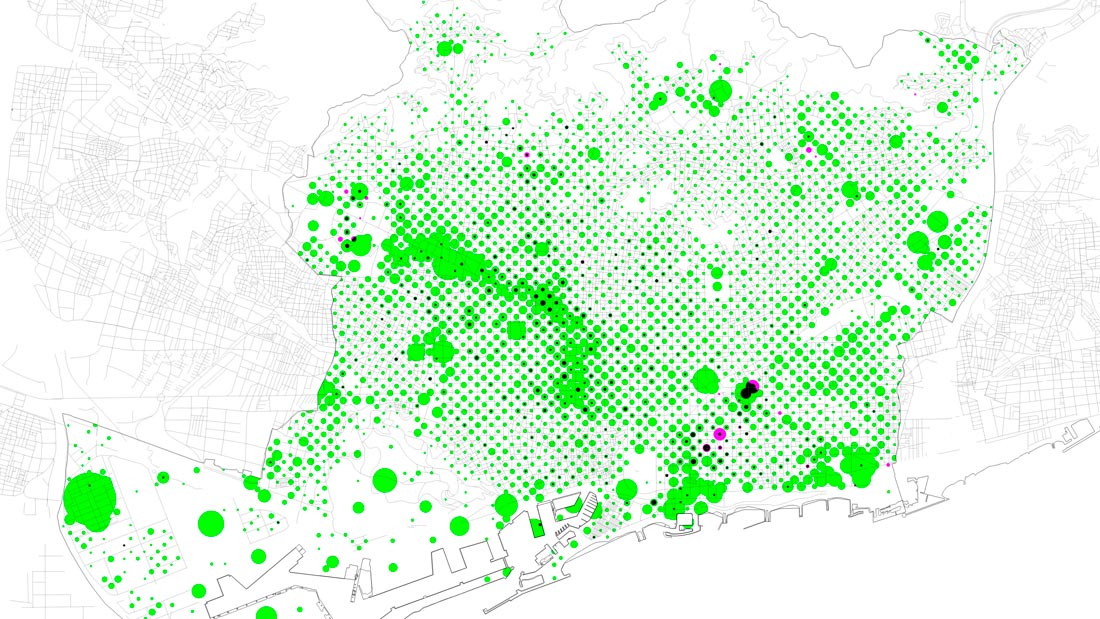
Economic background. Proportion of innovative initiatives (magenta) with respect to number of companies (green).
Urban context. Surface of plots.
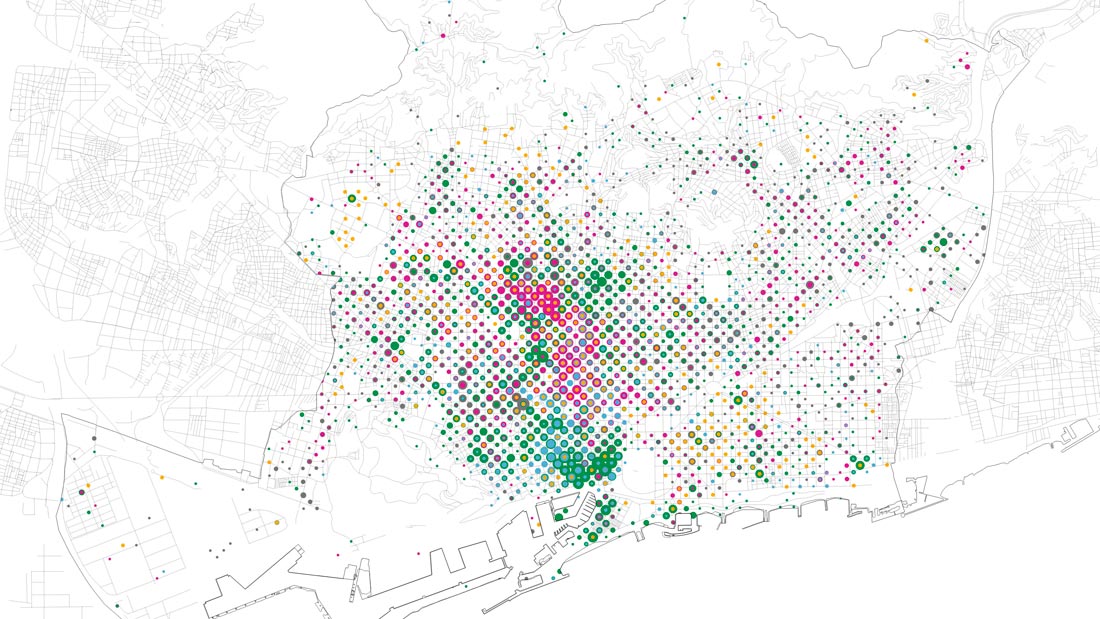
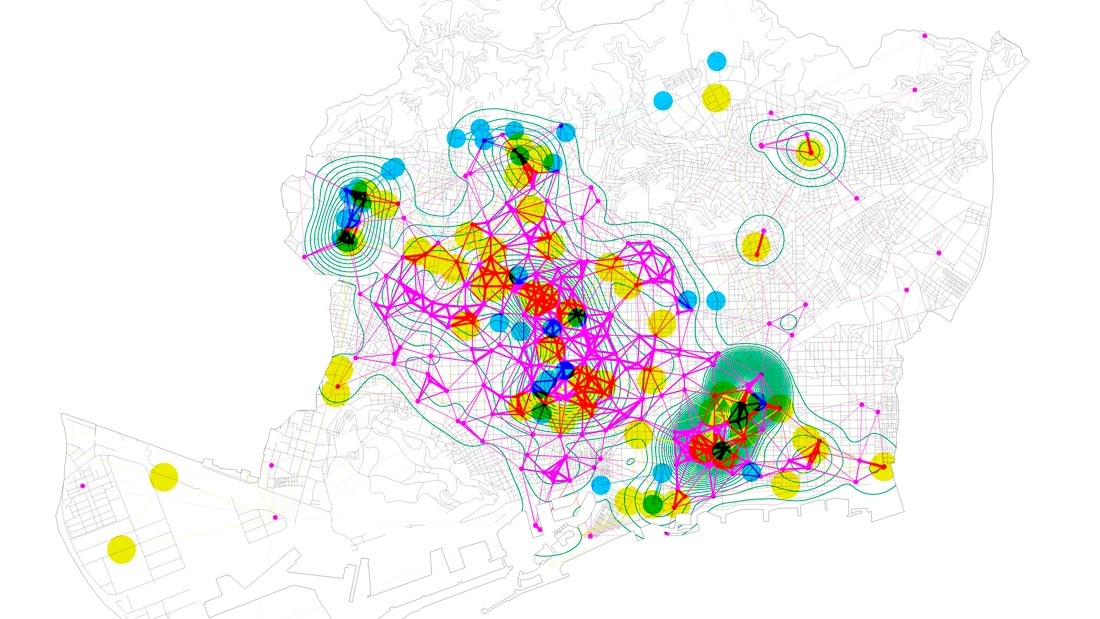
Urban context. Use of land where innovative initiatives are placed: cultural (yellow), office (cyan), commercial (magenta), green (industry), housing (grey).
Barcelona has more than 700 innovative startups, leader companies and research centers focusing primarily in the areas of new technologies, health and digital fabrication. One of the strengths of this model is the apparently uniform distribution of innovation facilities throughout the city. Urban and environmental conditions (compactness, good communication, cheap rentals, diversity of local services, etc.) influence the location of innovative initiatives, although these conditions are not always decisive – each activity requires certain specific conditions.
Urban context. Local services: innovative initiative (yellow), hotel (blue), finance (fuchsia), bar and restaurant (green), shops (grey).
Accessibility to public transportation.
Representativeness.
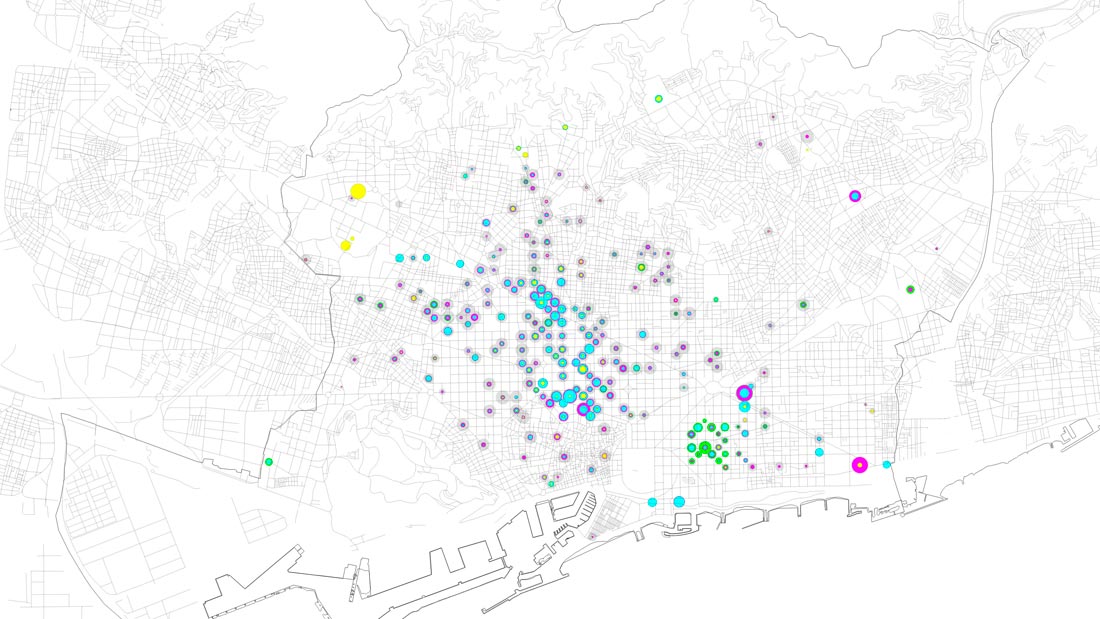
Innovation occurs around leader companies and research centers according to three spatial models: line, along main civic axes; network as the 22@ district and centers, in research clusters and university campuses. In the first two cases, despite reflecting opposite situations (an area that concentrates representativeness and economic power with respect to a district with low rentals and a large premises), innovative initiatives take advantage of centrality and mixed-use. However, research campuses are not always able to bring together a significant number of initiatives as often university facilities are placed in areas with less favorable urban conditions.
Level of attractiveness of leading companies and research centres.
Innovation network. Startup (magenta), research centre (blue), leading company (yellow).
In this sense, the innovation ecosystem of Barcelona, based on a diverse and compact urban fabric that enables a positive transference of innovation and knowledge to different parts of the city, could become a reference for other urban areas.