This project visualizes a relatively new phenomenon: online free expression in China. It examines some innovative strategies employed by users of Weibo, a Twitter–like micro–blogging platform.In collaboration with Penn Voices, Brown Institute, School of Journalism and Propublica.
Use of the Internet in China is policed — watched over, censored, and punished — by a human and technological program that has been nicknamed ‘The Great Firewall’. The aim is to keep politically unacceptable or “sensitive” content (words and articles about the Tiananmen Square massacre, for example) invisible to Chinese Internet users. Twitter and Facebook are largely blocked, as are many news outlets and human rights web sites; web searches are seriously curtailed; sensitive words are blocked; and online postings and other content is routinely removed, blog posting removed. For many Chinese users who wish to access blocked web sites, the only option is a Virtual Private Network (VPN), a virtual leap over the Great Firewall.
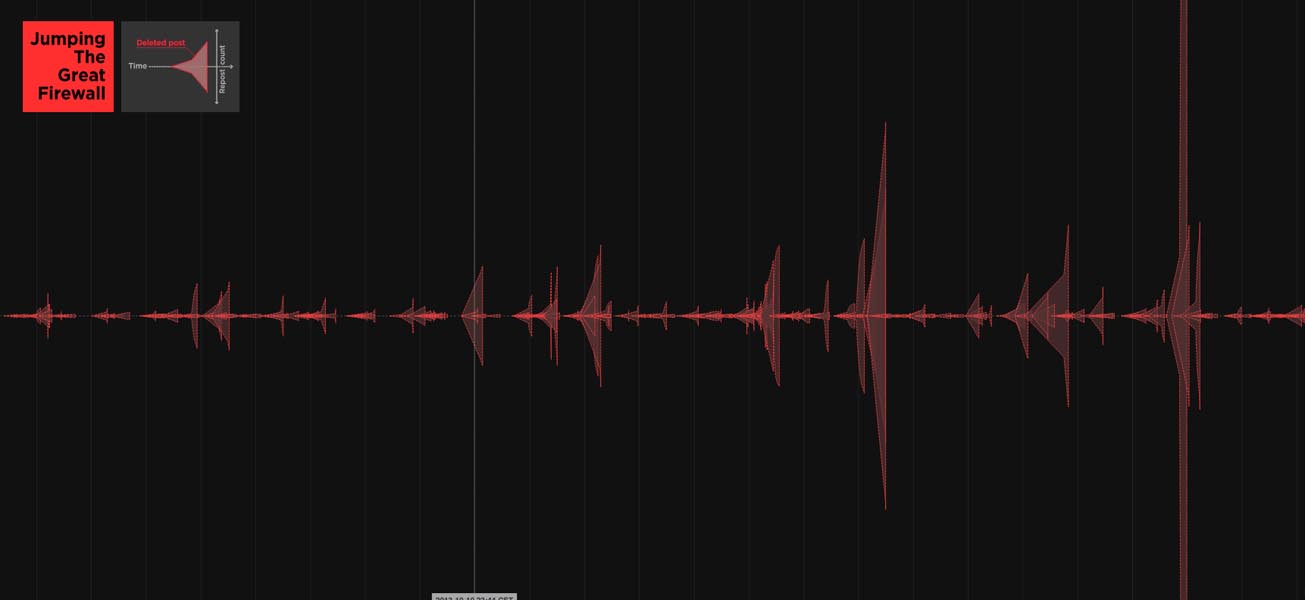
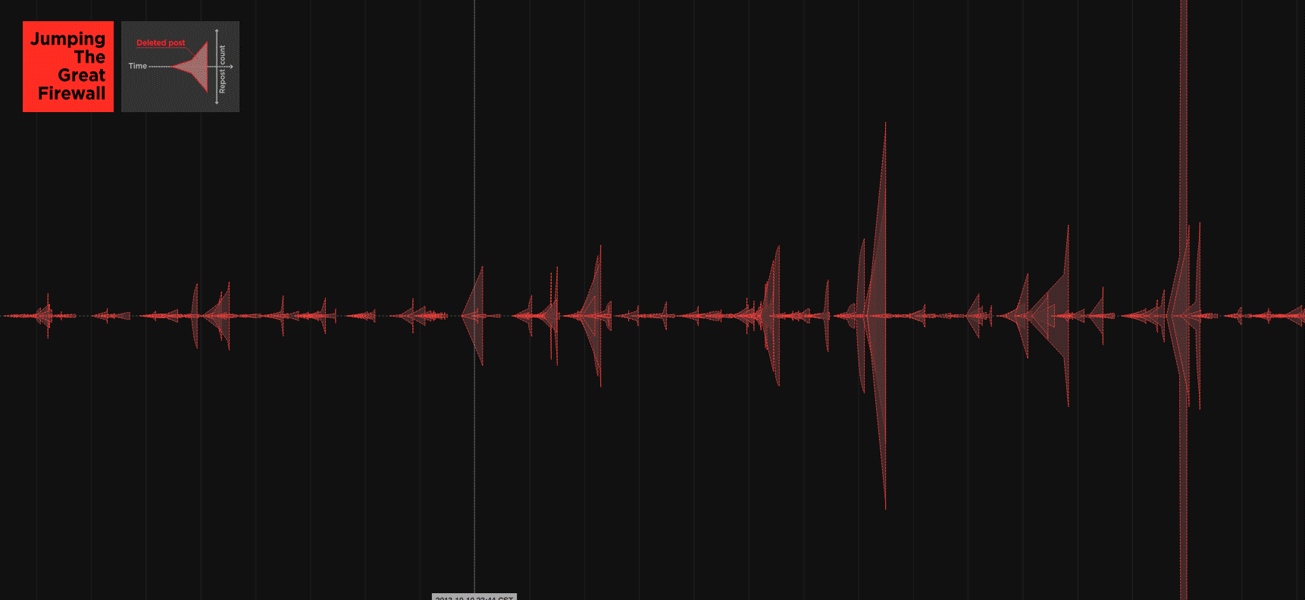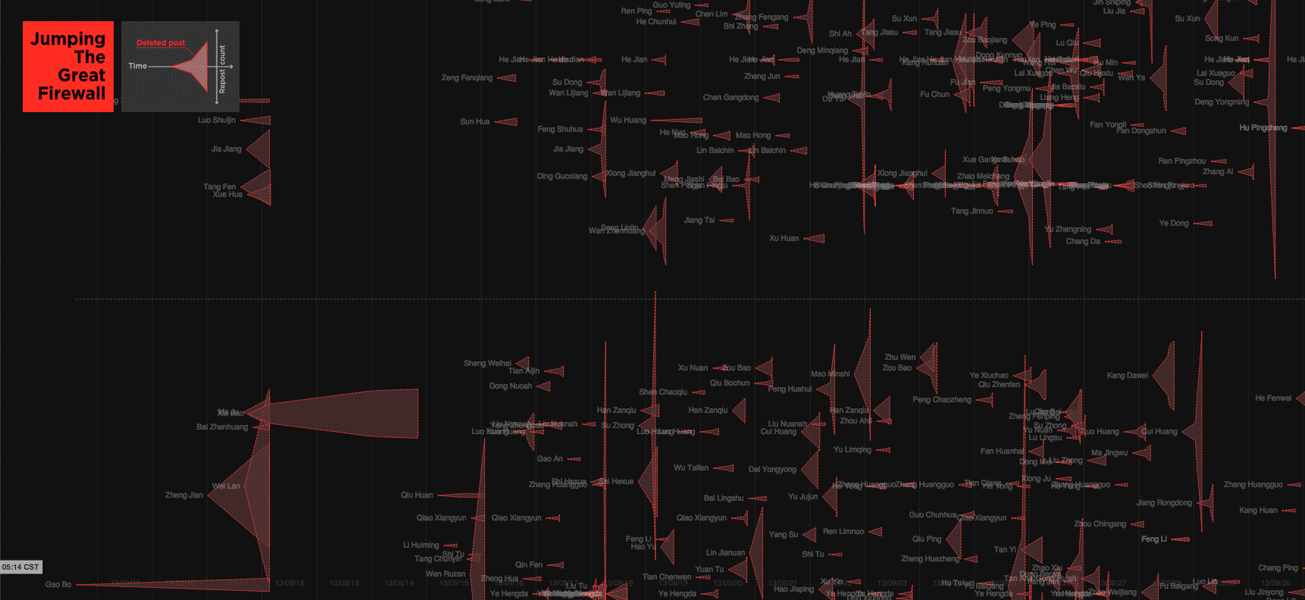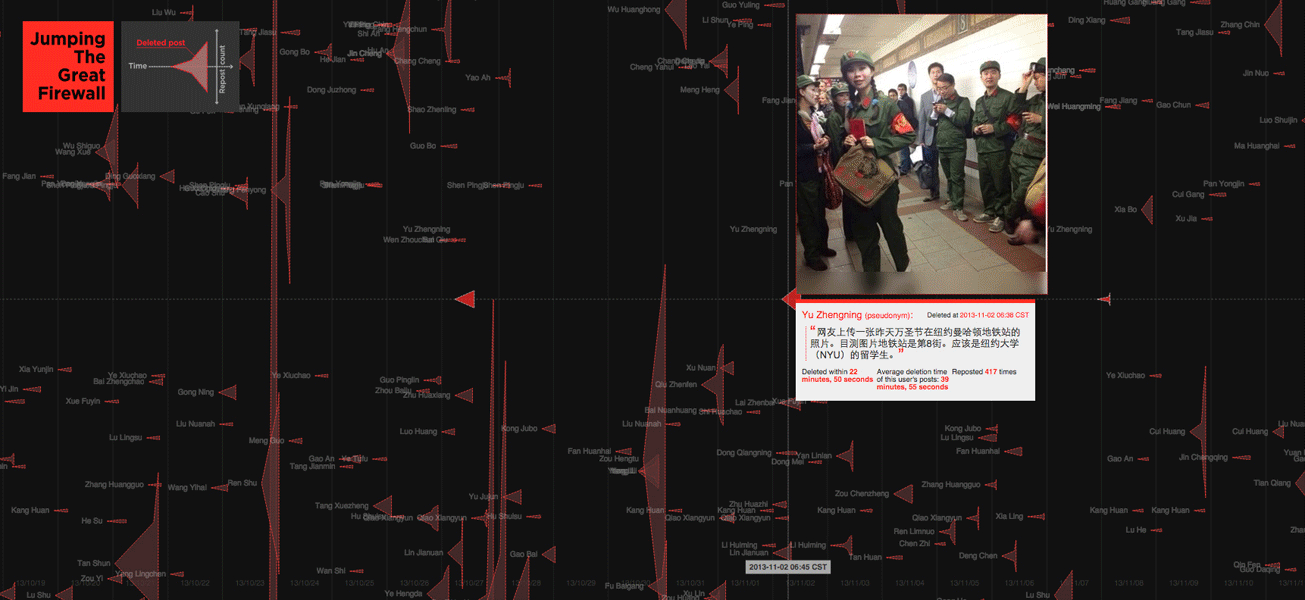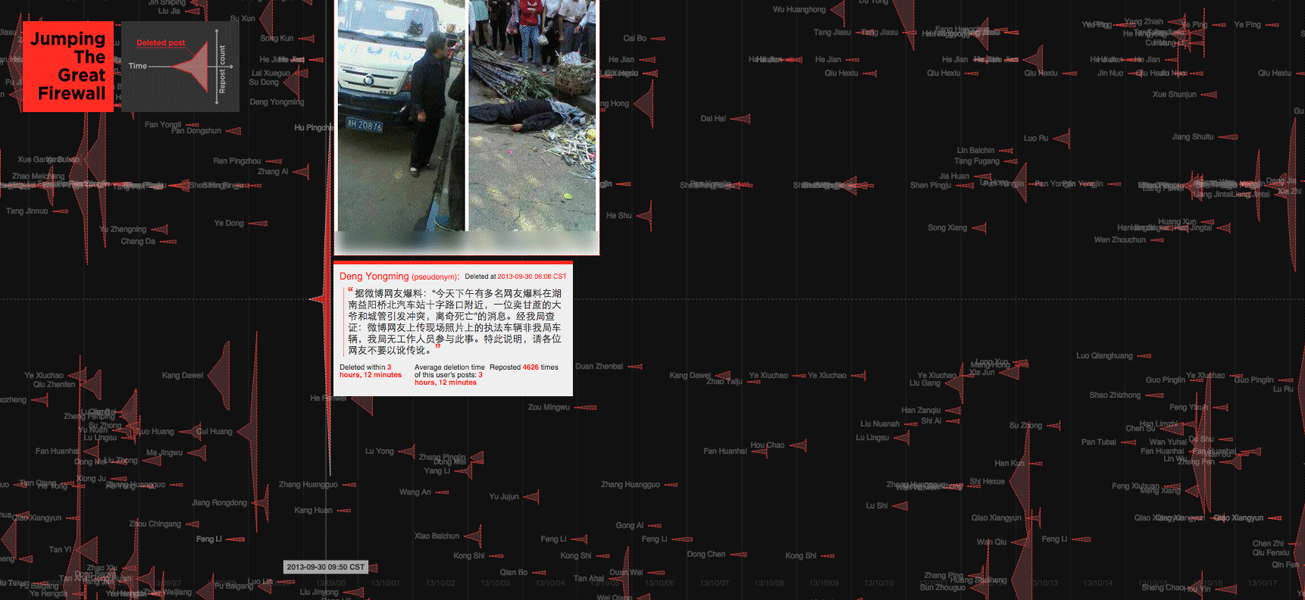
We examined a different strategy that has emerged in Weibo blogging, where users can insert images directly into their postings, without links. Images are much more difficult for automated search programs to analyze, which allows image-based content to spread more widely before it is detected and removed. Taking advantage of this, some users now turning writing into images, taking screenshots of their own and others’ controversial posts before they’re removed, then posting and re–posting them. Visualized here are many such deleted posts from September 8th to November 13th, in 2013.
Research for this investigation was conducted in collaboration with a team at the Spatial Information Design Lab and the Brown Institute for Media Innovation, in partnership with Pen American Center and ProPublica. The ProPublica article, called China’s Memory Hole: The Images Erased From Sina Weibo” uses a similar methodology to ours.