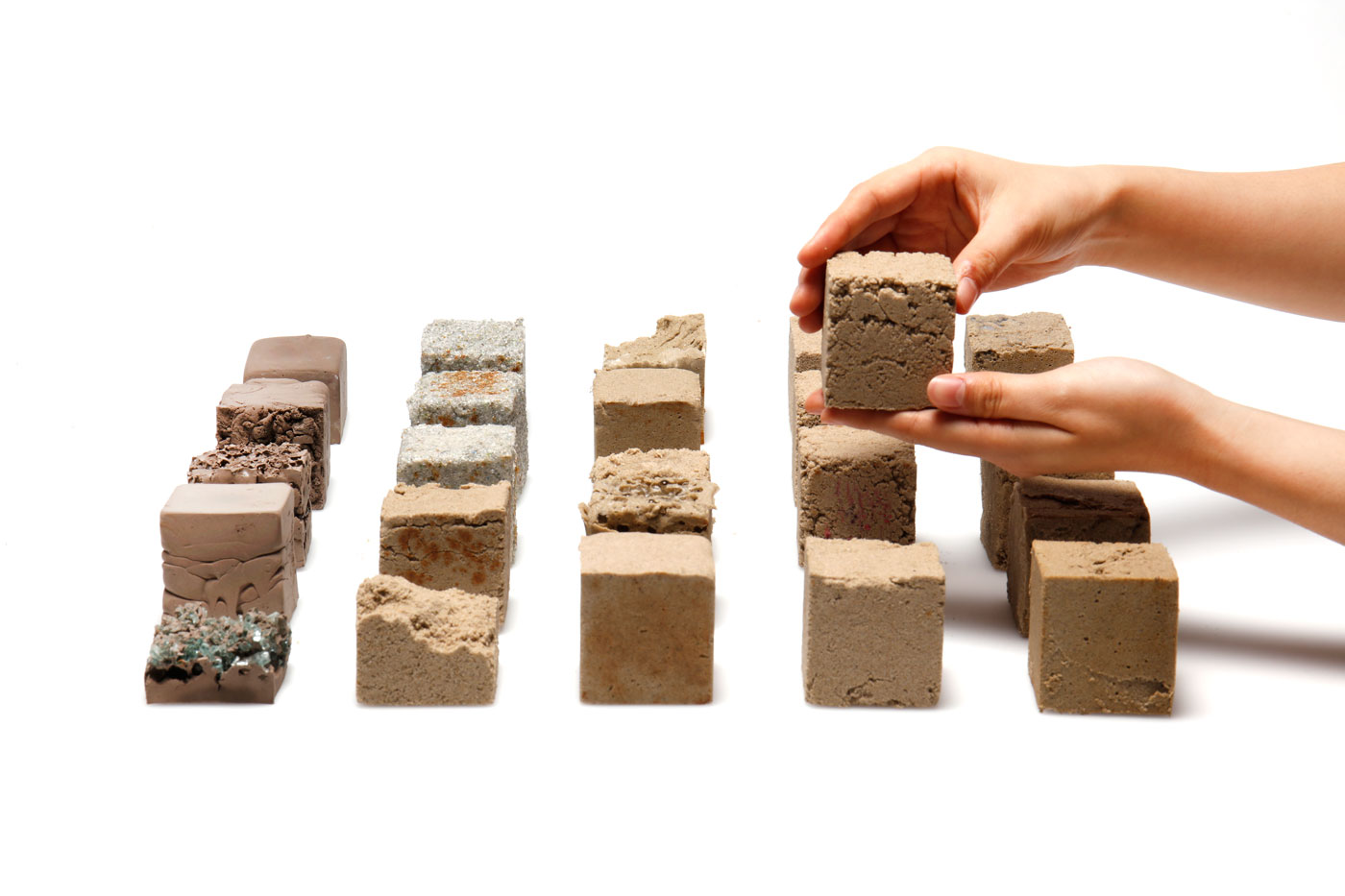
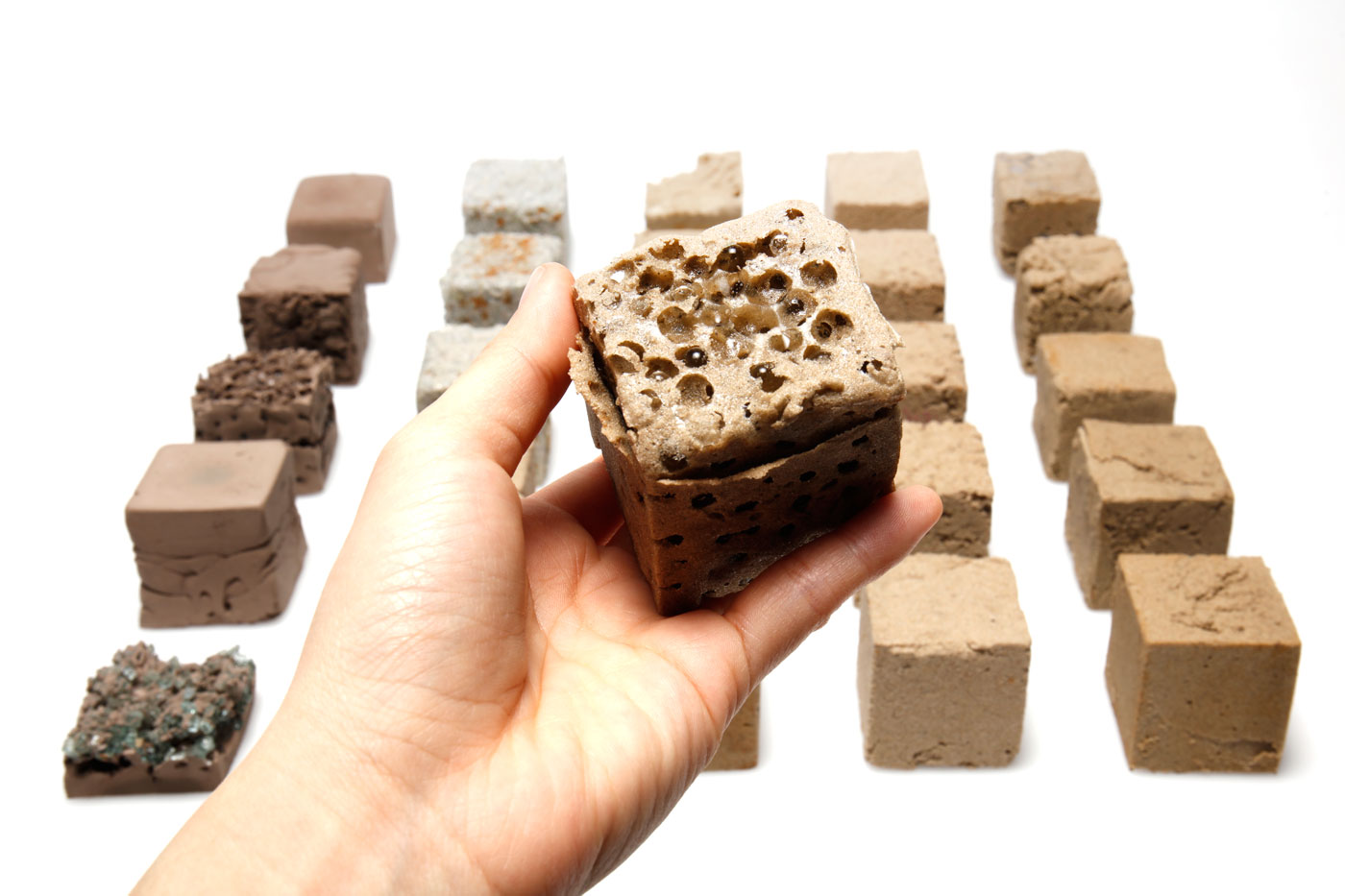
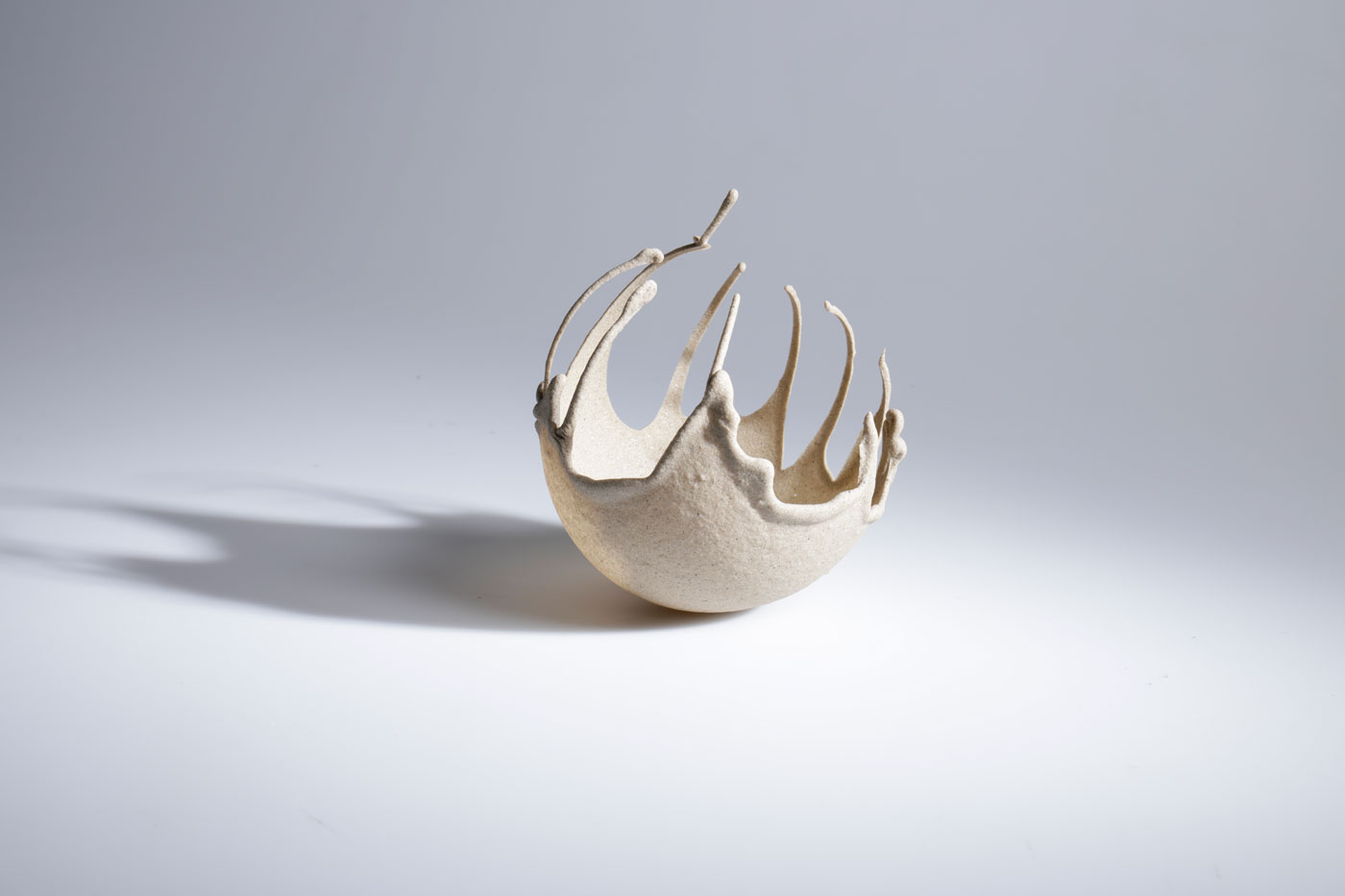
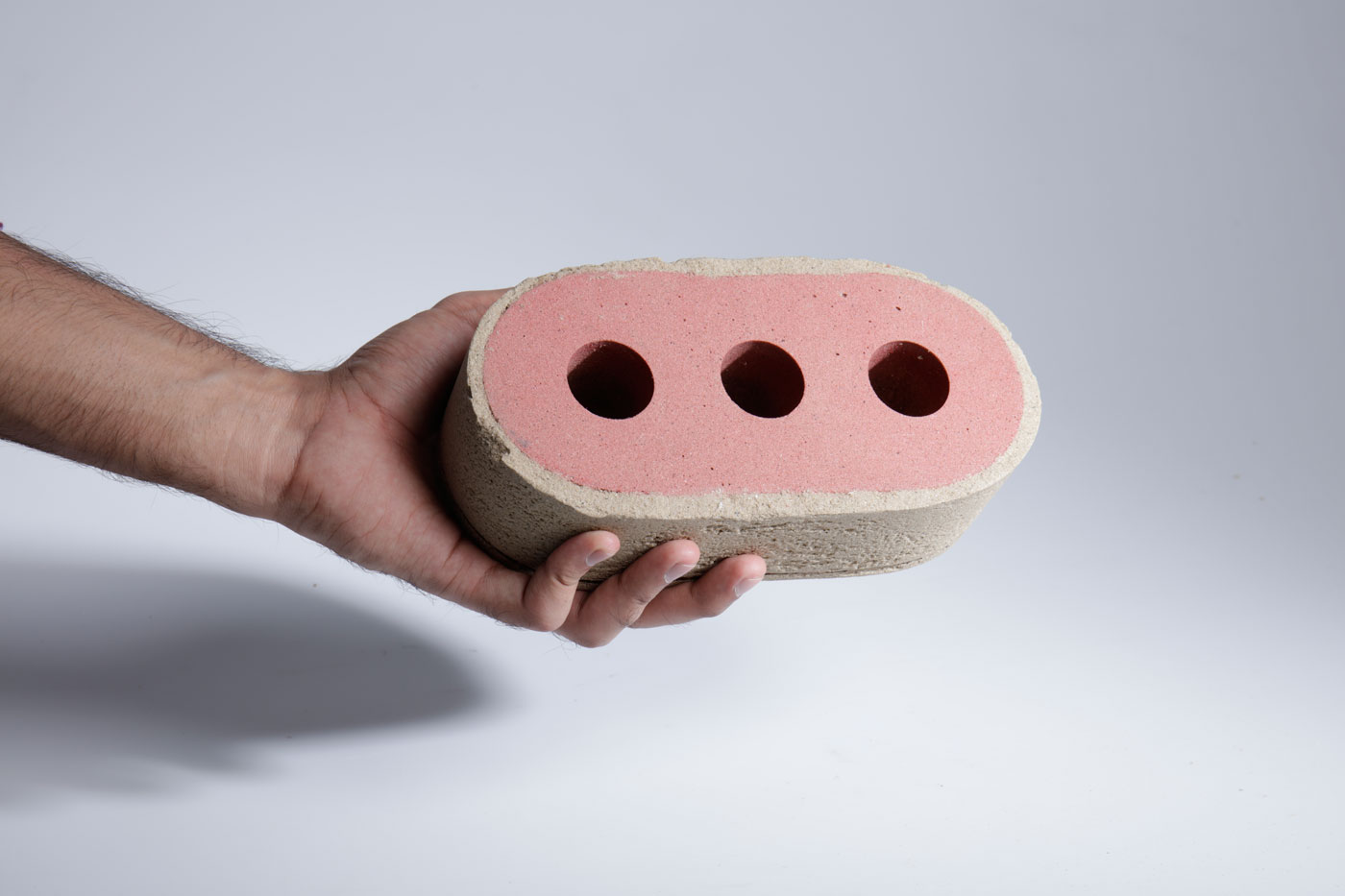
There is a common misconception that sand is an abundant resource. Beach, river and quarry sand are all in high demand and heavily used in many industries, especially construction. Desert sand however has little use, as its grains are too smooth and fine to bind together. Even Dubai imports sand from other countries. Finite however uses a new binder to help effectively bind together desert sand into structures.
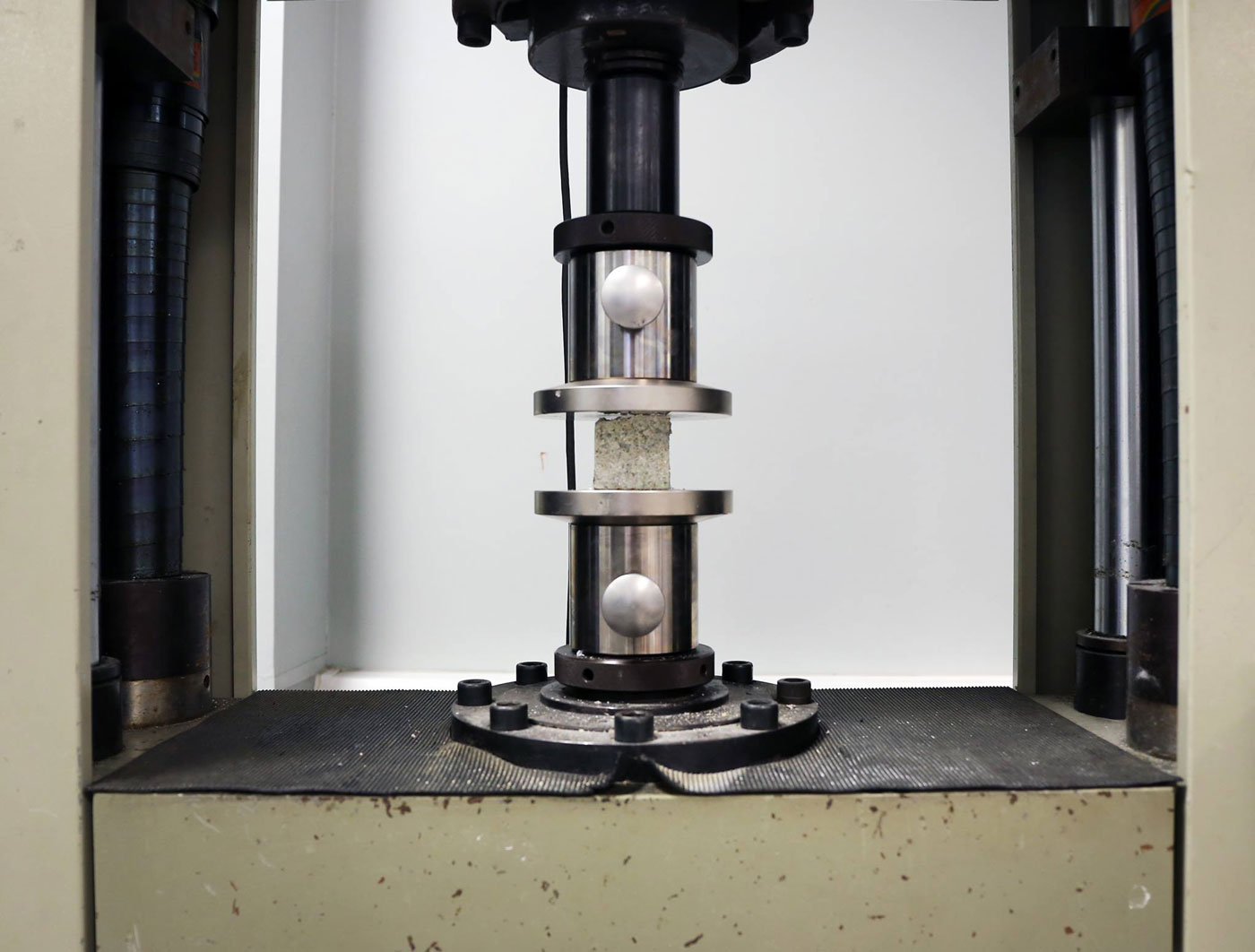
The development of Finite opens new opportunities to make use of desert sand and other abundant fine powders that traditionally have no use. Finite can be formed into sand structures that have the same strength as traditional housing bricks and even residential concrete. However, compared to both housing bricks and concrete, the process to make this material is simple and does not require extreme temperatures. Finite is environmentally friendly, with less than half the carbon footprint of concrete. Most impressively, thanks to its material properties, Finite can be easily reused and then remoulded for multiple lifecycle uses. The material can be coloured to create different aesthetics such as marbling to suit the desired application, producing intricate and smooth finishes.
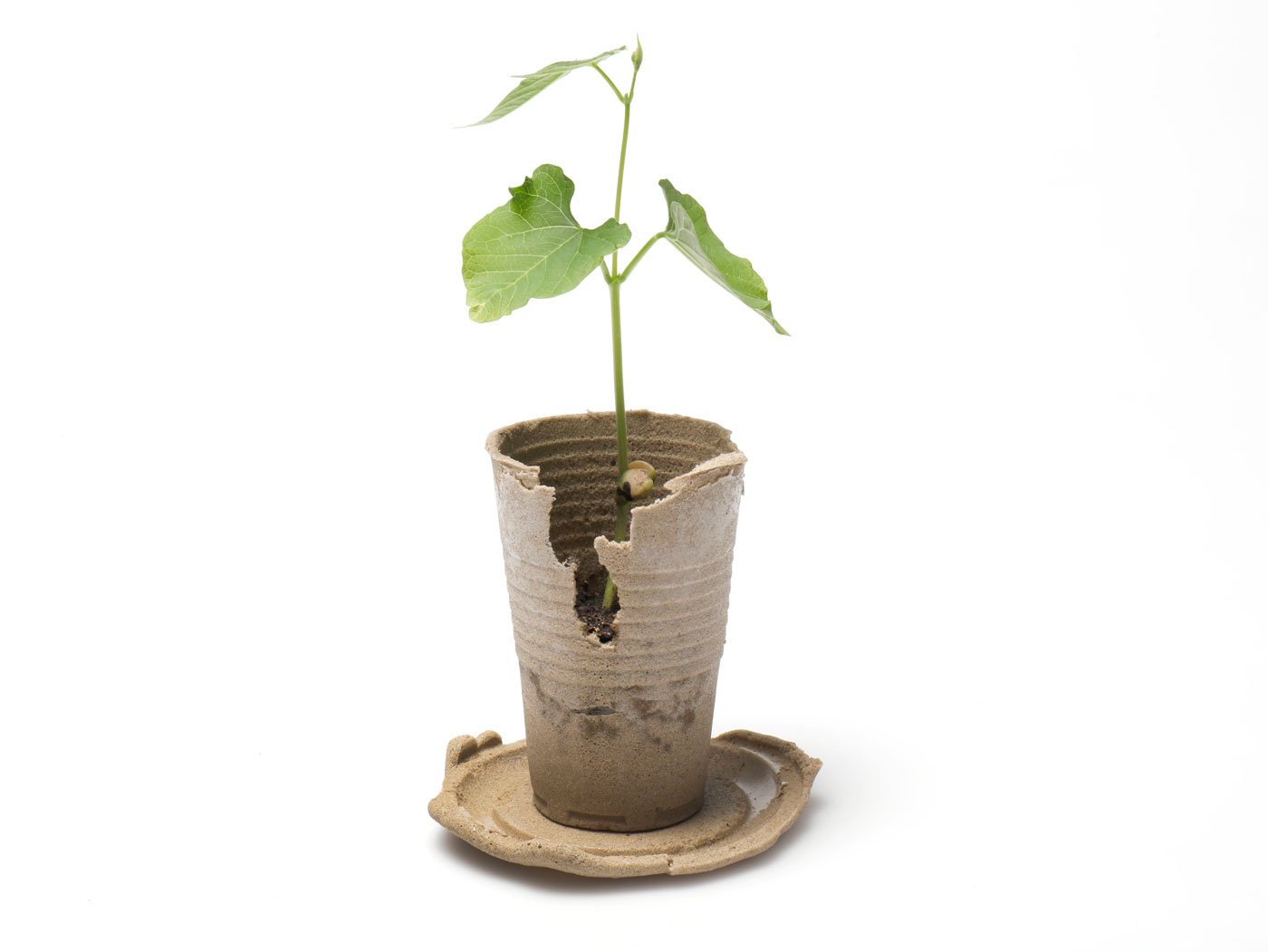
This material’s reusability and sustainable end of life has led the team to explore its application in short-term infrastructure projects. Structures using Finite would be made from abundant local fillers using a simple process. Once these structures are no longer needed, they could be quickly deconstructed thanks to their design and the material’s unique properties. The deconstructed material could then be collected for reuse, or left on-site to safely biodegrade back into the local environment.
With the continued interest and support of experts, work will continue on developing manufacturing processes and applications such as on-demand desert roadways and durable refugee shelters. The team hopes this composite material will demonstrate the power of building with abundant and reusable natural materials and hopefully relieve demand on overexploited ocean and river sands.